1. Metagenomic sequence collection, plasmid extraction, and clustering.
To do this, we collected 212,560 publicly available human metagenomes, along with metadata, from four major body sites: skin, oral cavity, gut, and vagina. After removing low-quality assemblies, we employed Genomad, Plasmer, and Platon to extract plasmid sequences, resulting in a final dataset of over 1 million high-confidence plasmid sequences. The resulting plasmid sequences were clustered together with reference sequences from PIPDB and our own de novo assemblies, using an average nucleotide identity (ANI) threshold of > 95%. This process yielded a total of 19,078 plasmid clusters.
2. Understanding PlasmidVar mutation detection tools
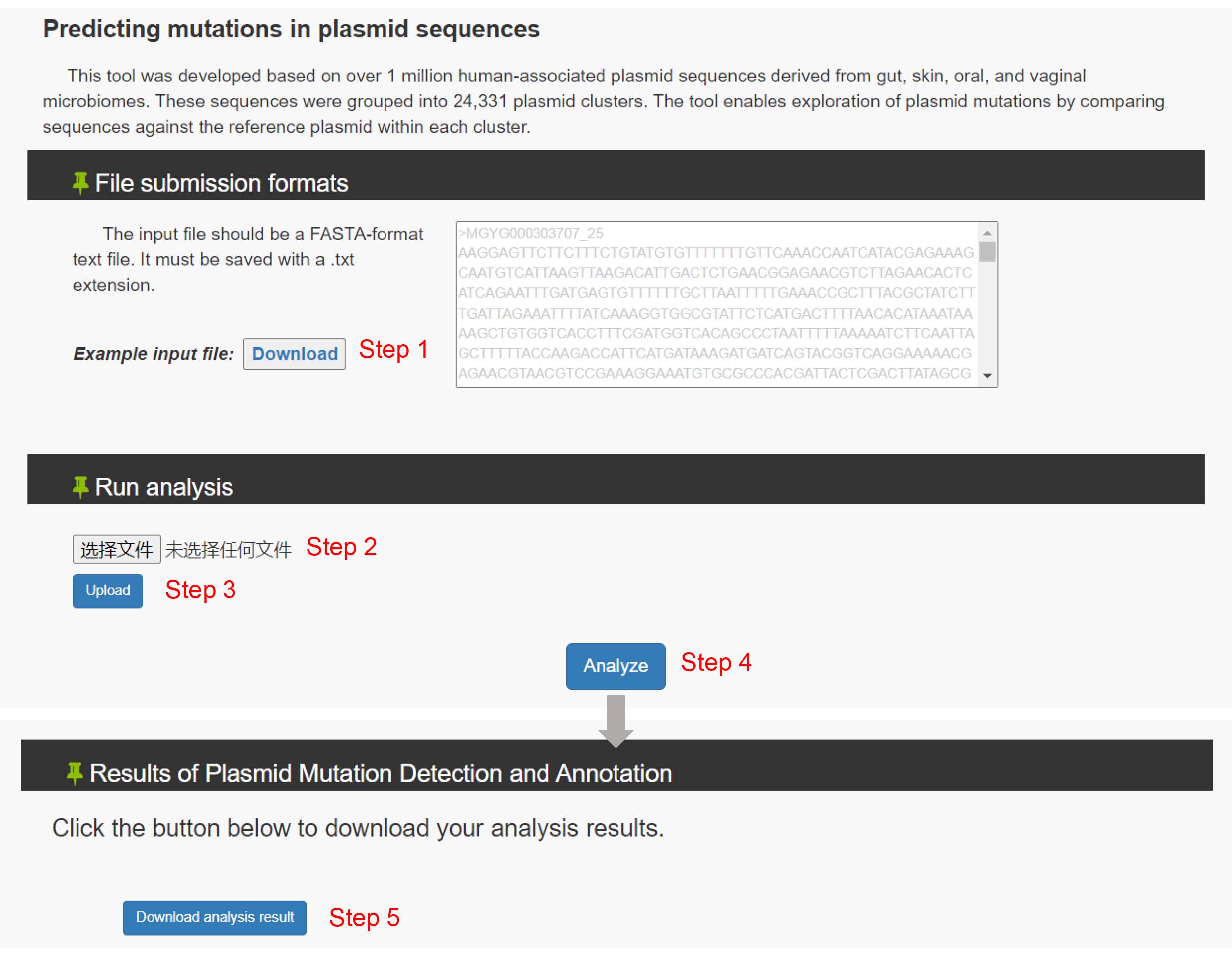
3. Understanding PlasmidVar mutation annotation categories
Search page, example: N501Y (Protein level)
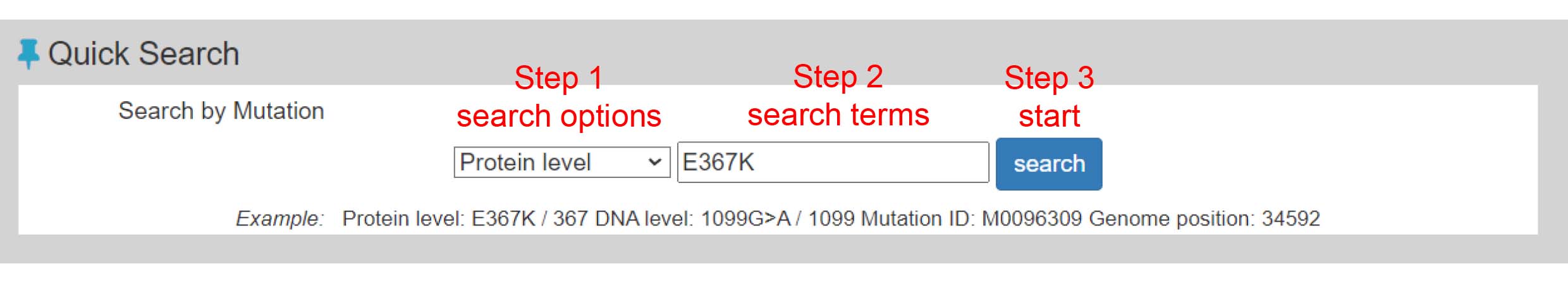
Search result table

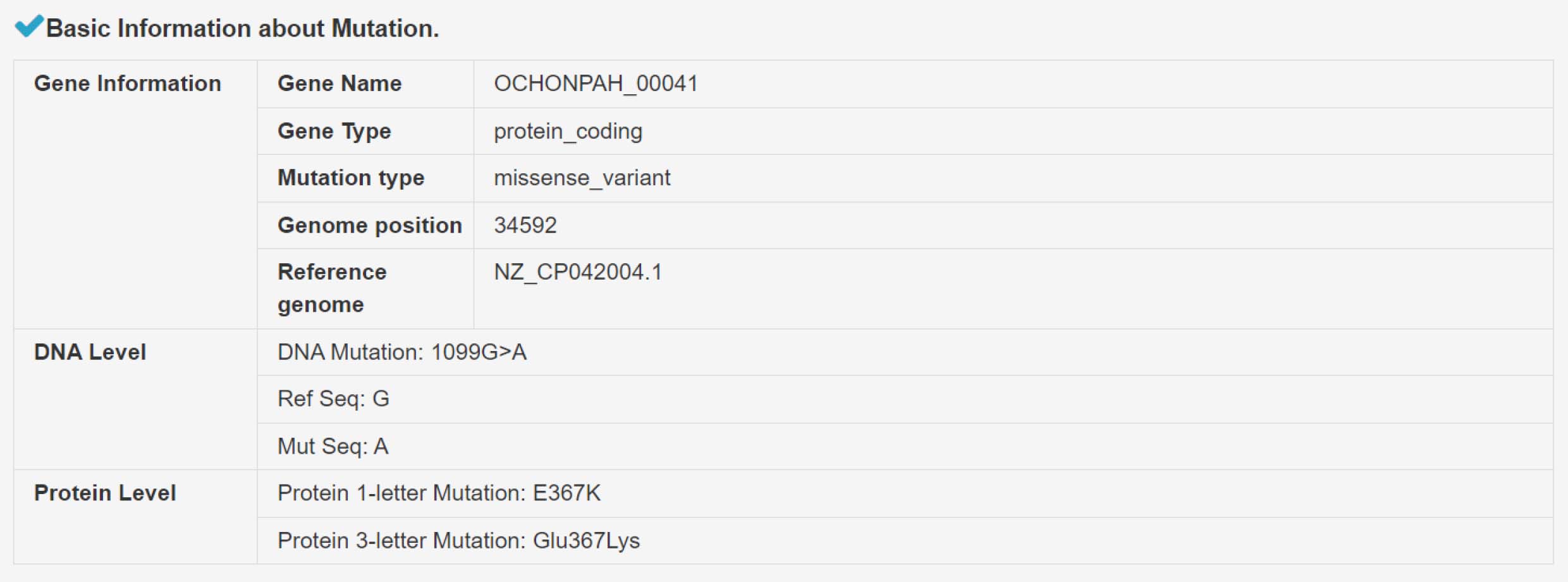
Mutation annotation result page

1) Summary information of mutation category

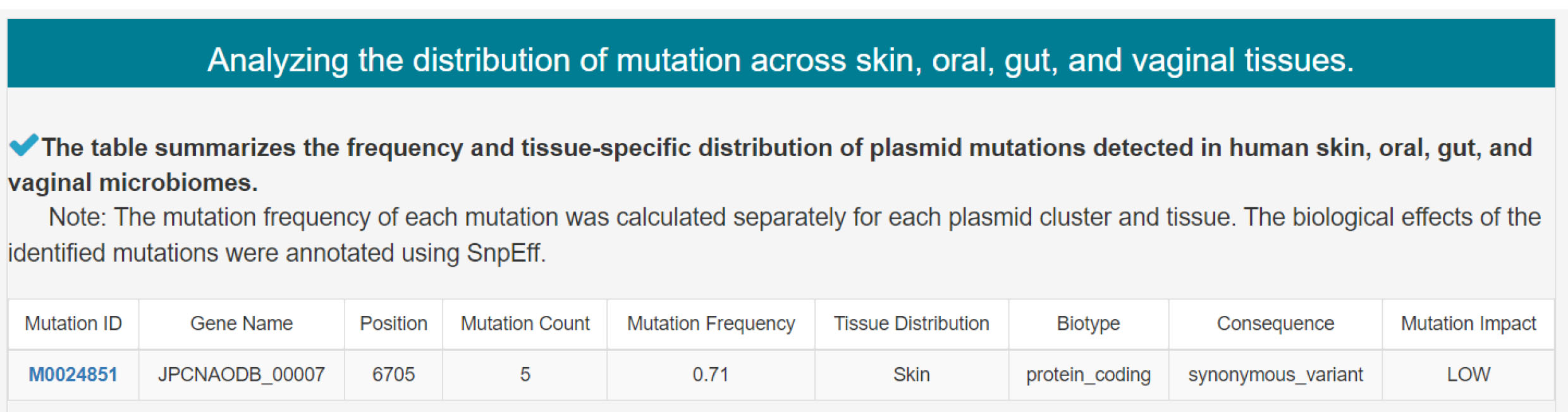
2) Analyzing the distribution of mutation across skin, oral, gut, and vaginal tissues
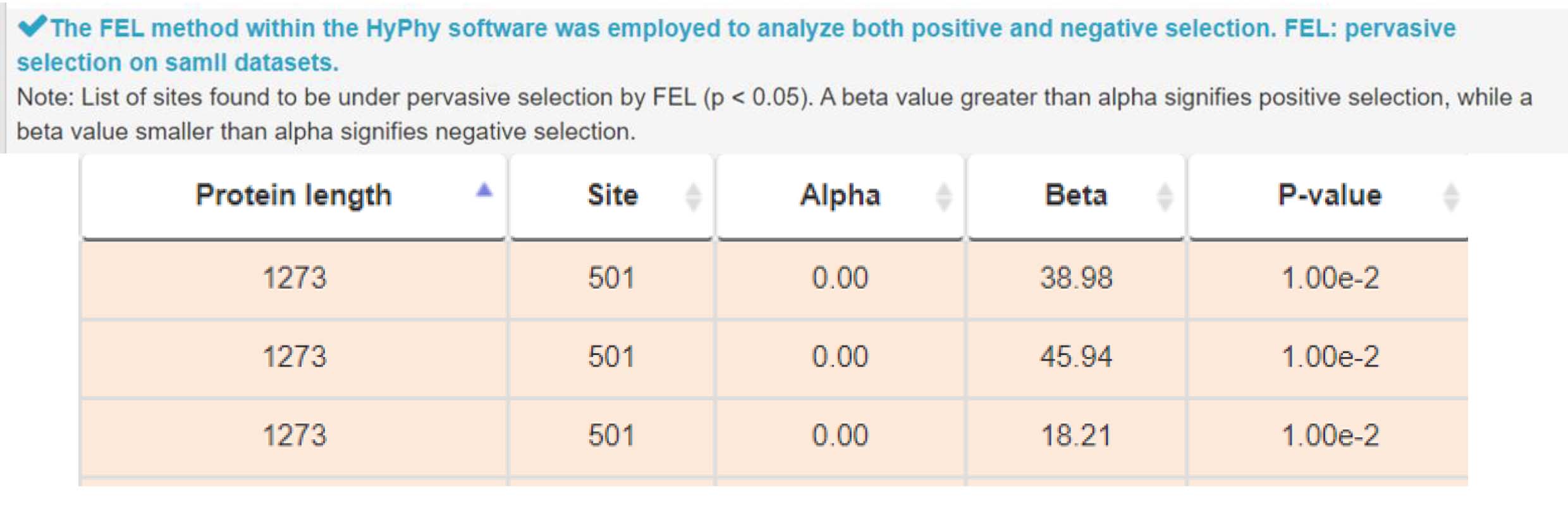
3) Investigating natural selection at mutation site for genetic adaptation and diversity
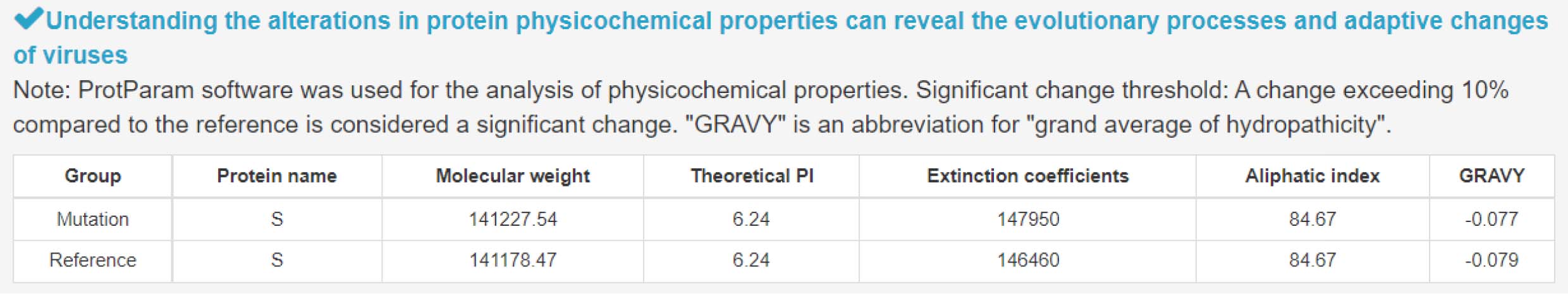
4) Alterations in protein physicochemical properties induced by mutation
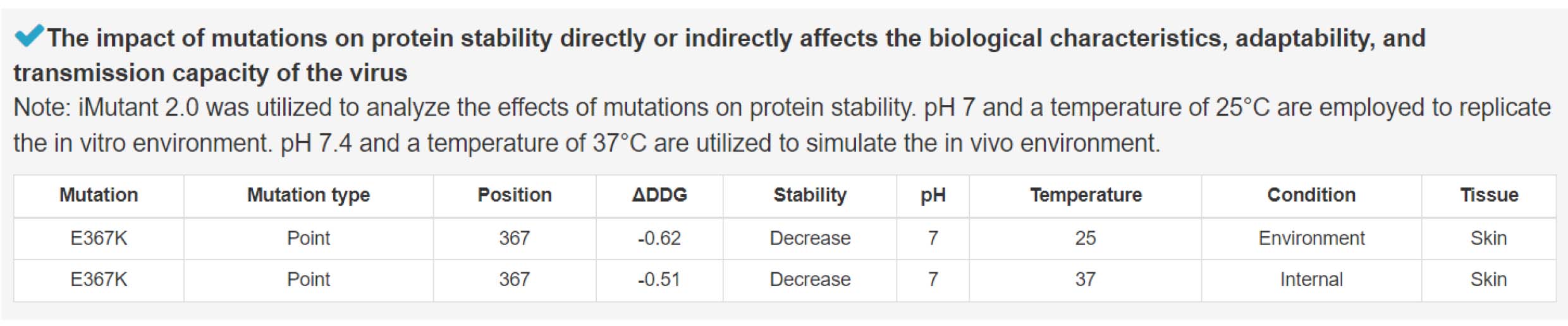
5) Alterations in protein stability induced by mutation
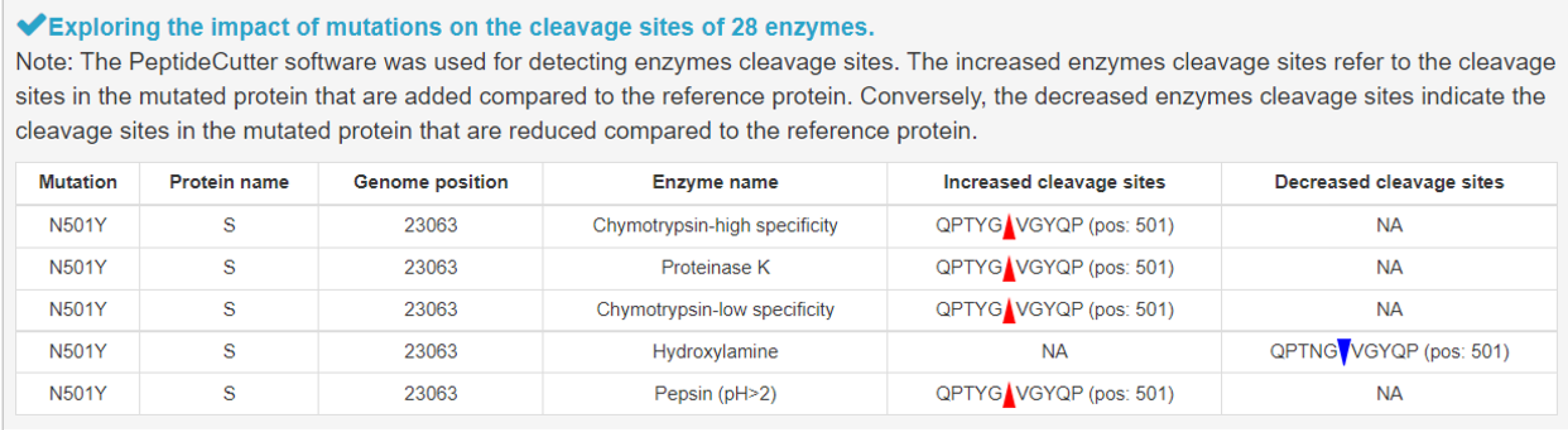
6) Alterations in enzyme cleavage sites induced by mutation
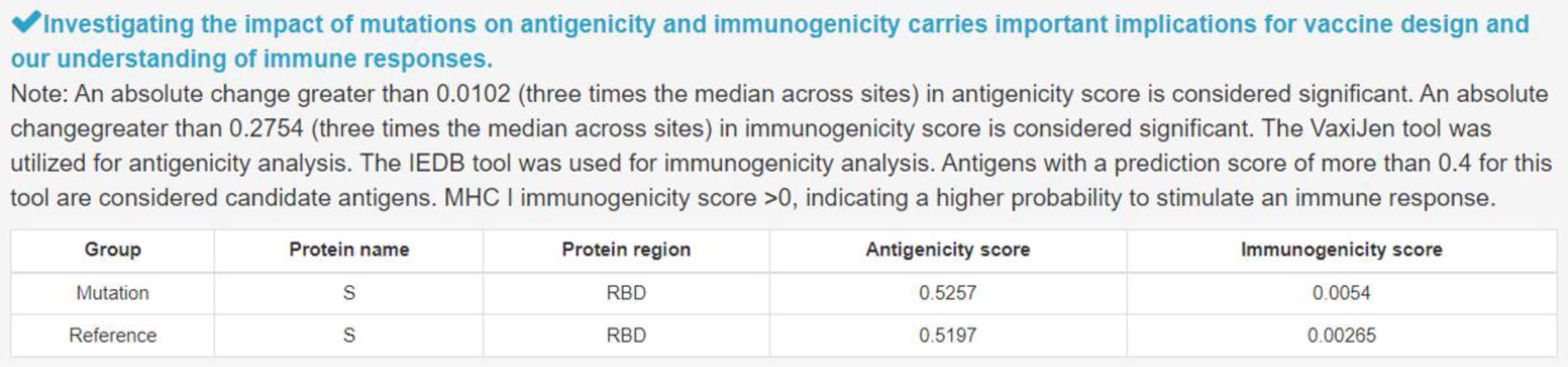
7) Impact of mutation on antigenicity and immunogenicity
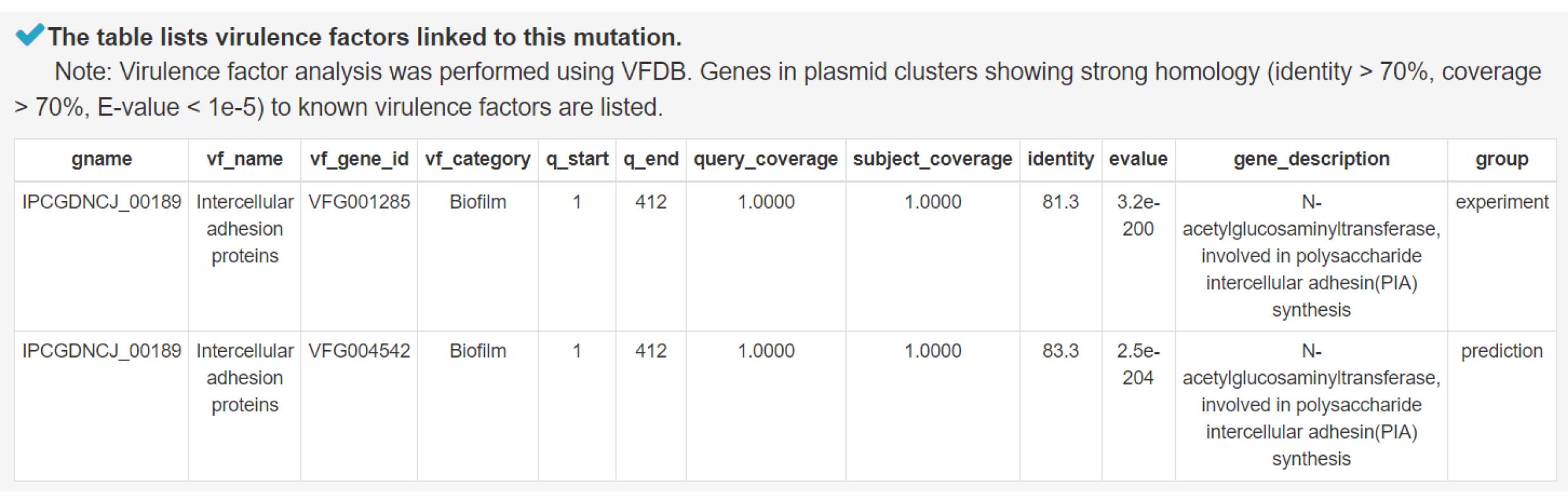
8) Analysis of virulence factors contributing to bacterial pathogenicity
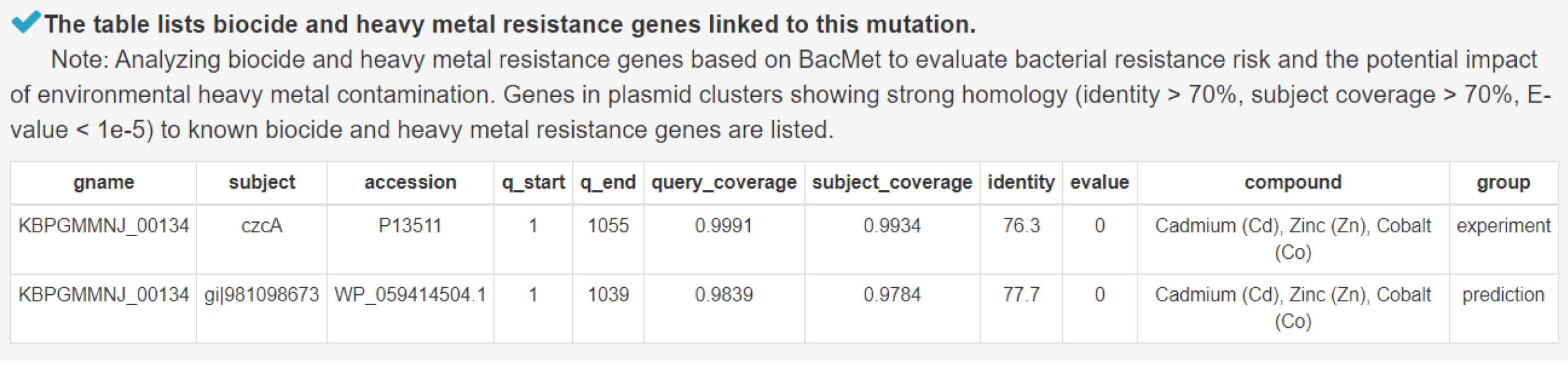
9) Analysis of biocide and heavy metal resistance genes to assess antimicrobial risk and environmental impact
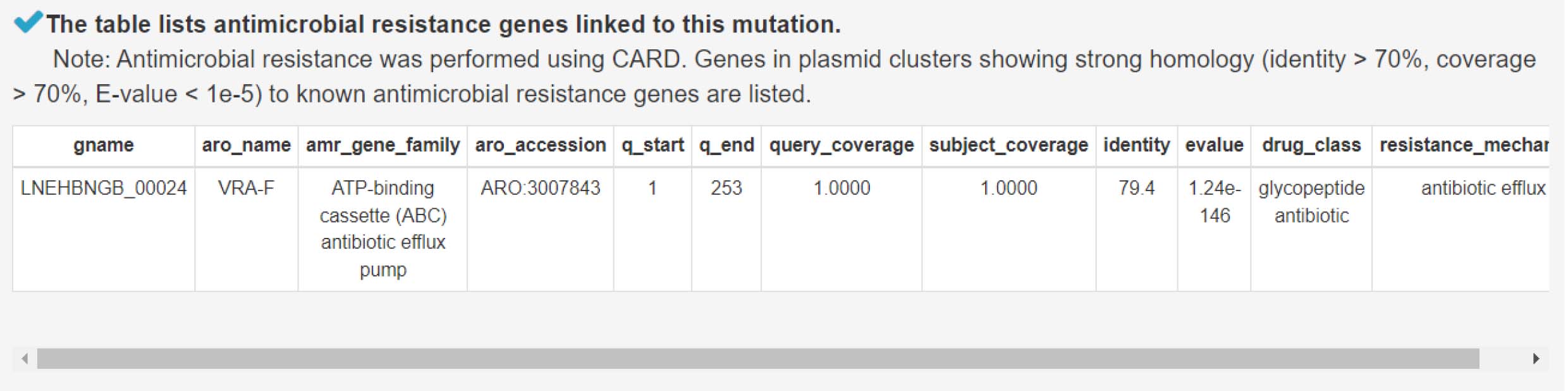
10) Analyzing antimicrobial resistance genes to assess bacterial resistance to antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents
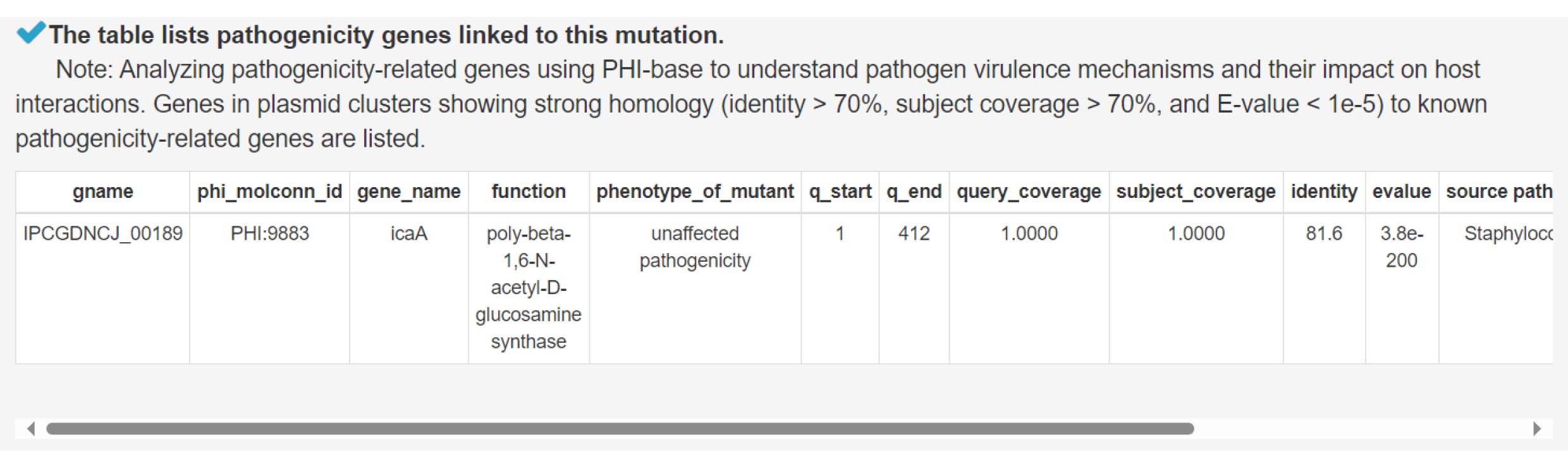
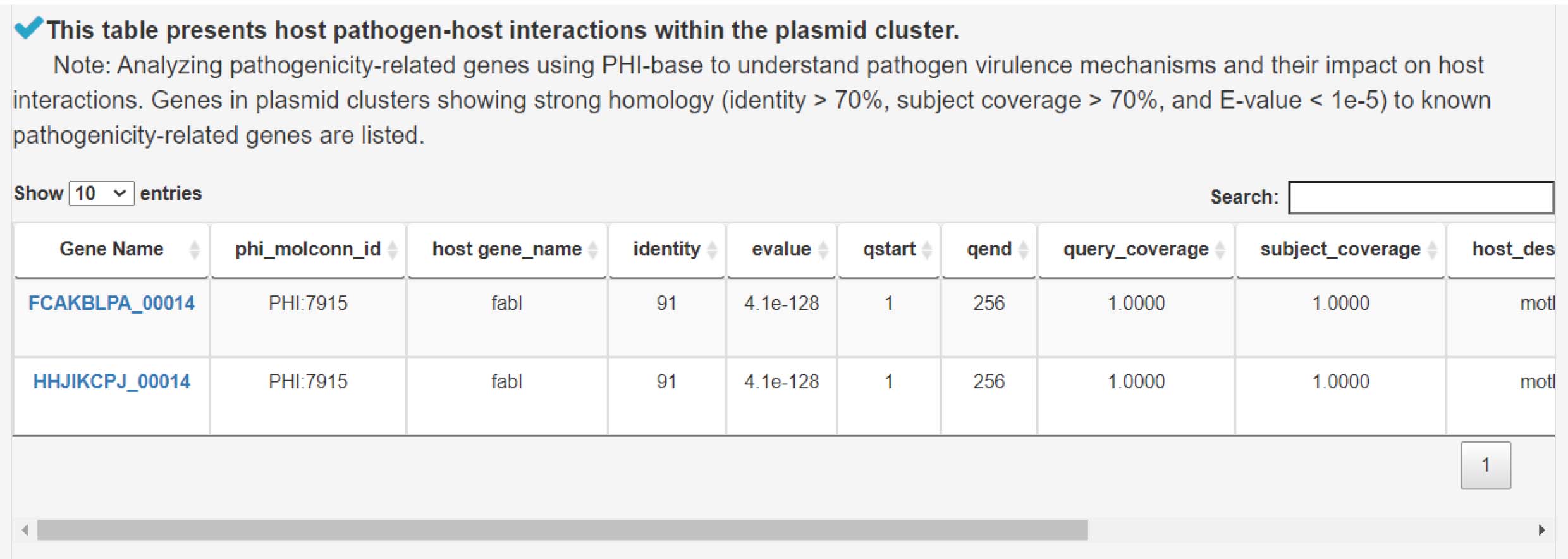
11) Analysis of pathogenicity genes to explore pathogen-host interactions
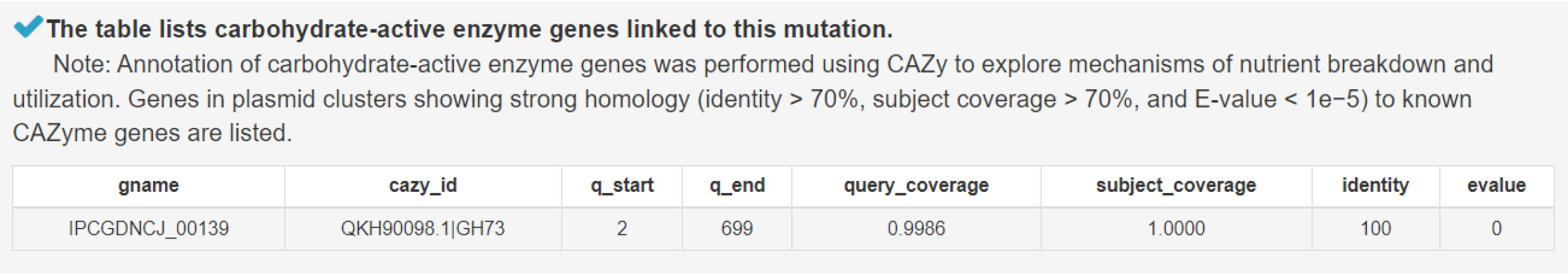
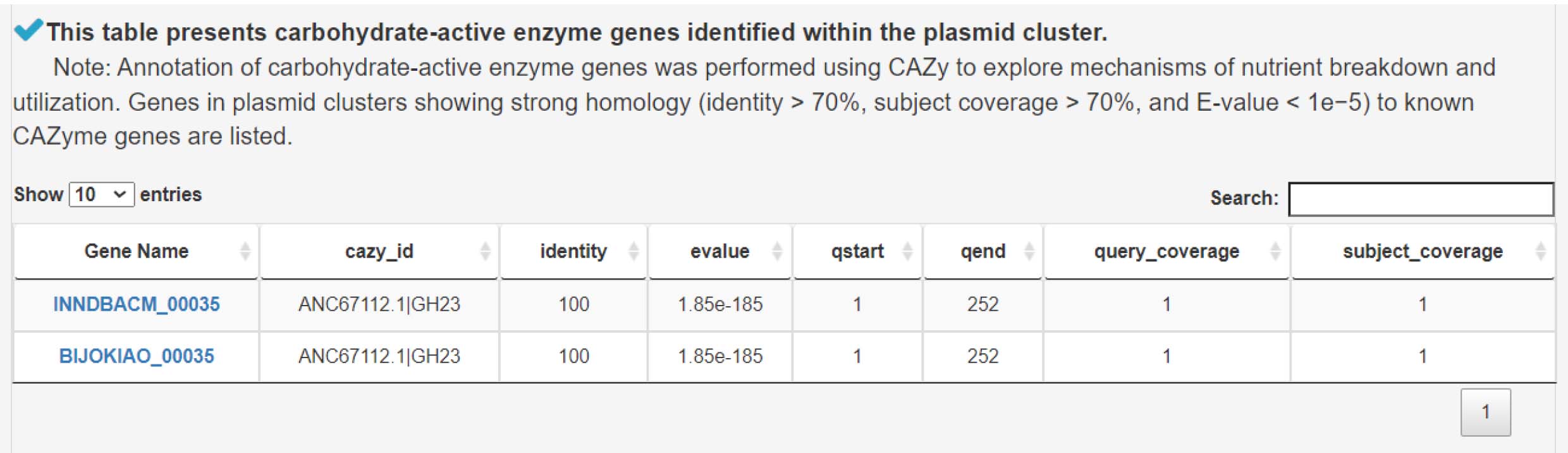
12) Analyzing carbohydrate-active enzyme genes to uncover mechanisms of nutrient degradation
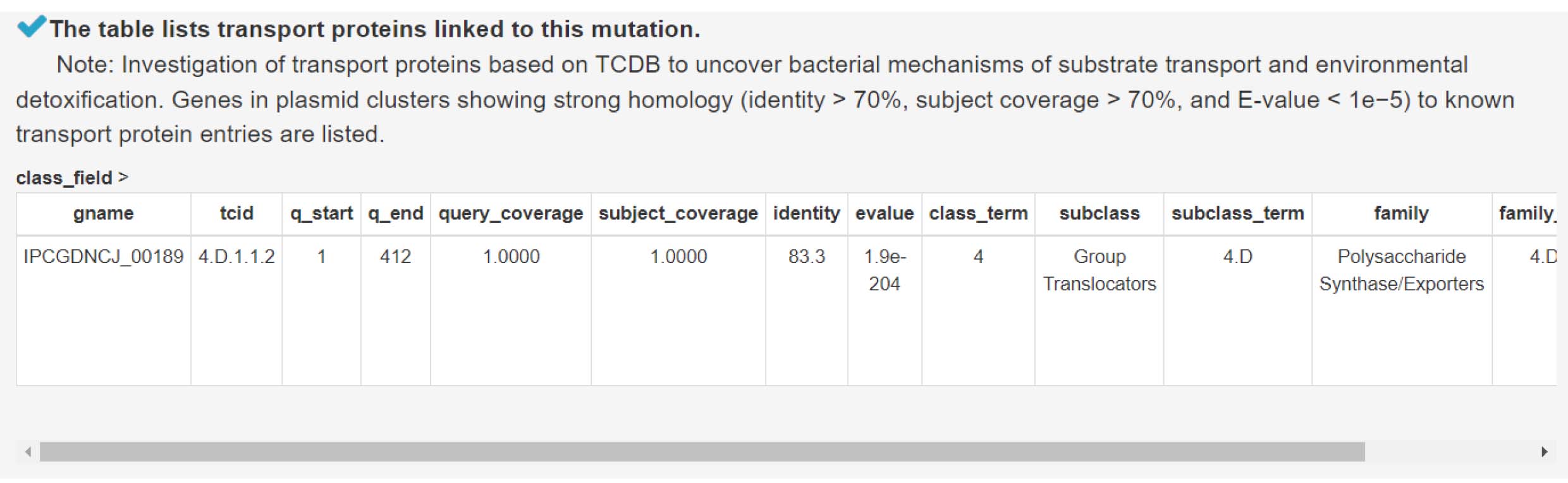
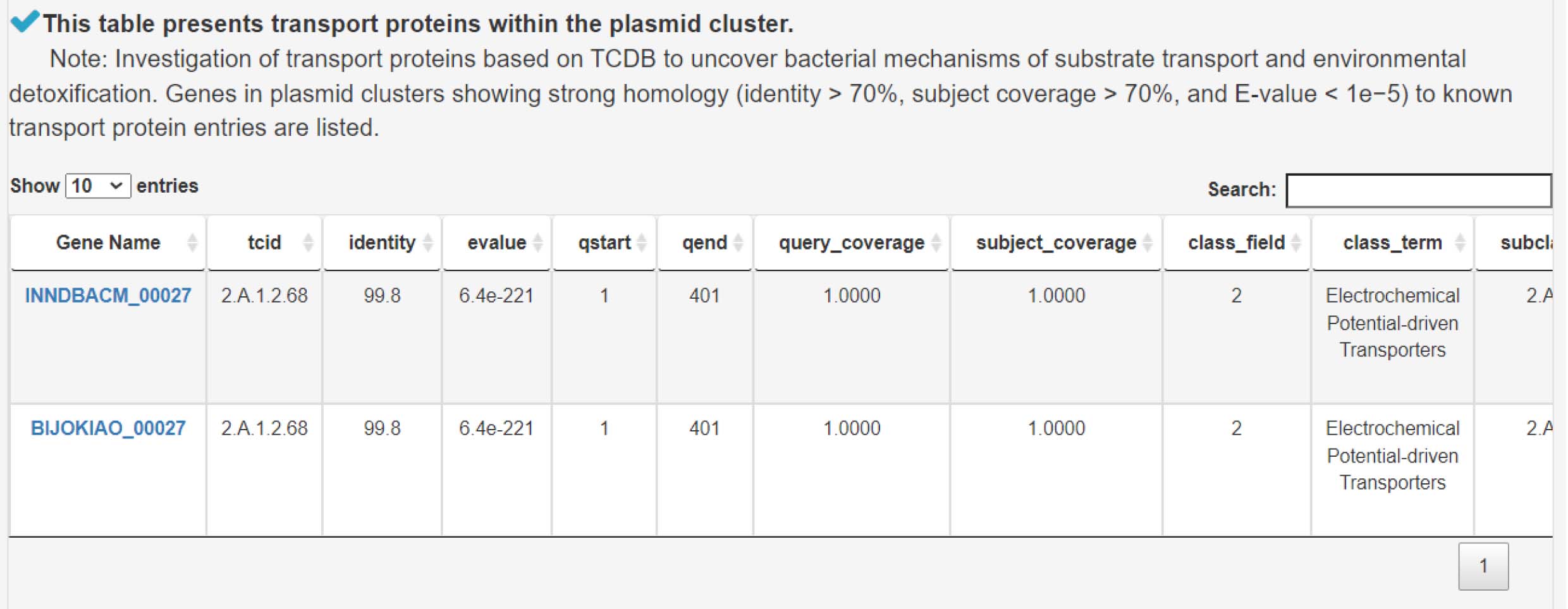
13) Analyzing transport proteins to understand bacterial strategies for substrate uptake and detoxification
4. Understanding PlasmidVar Cluster Annotation Categories
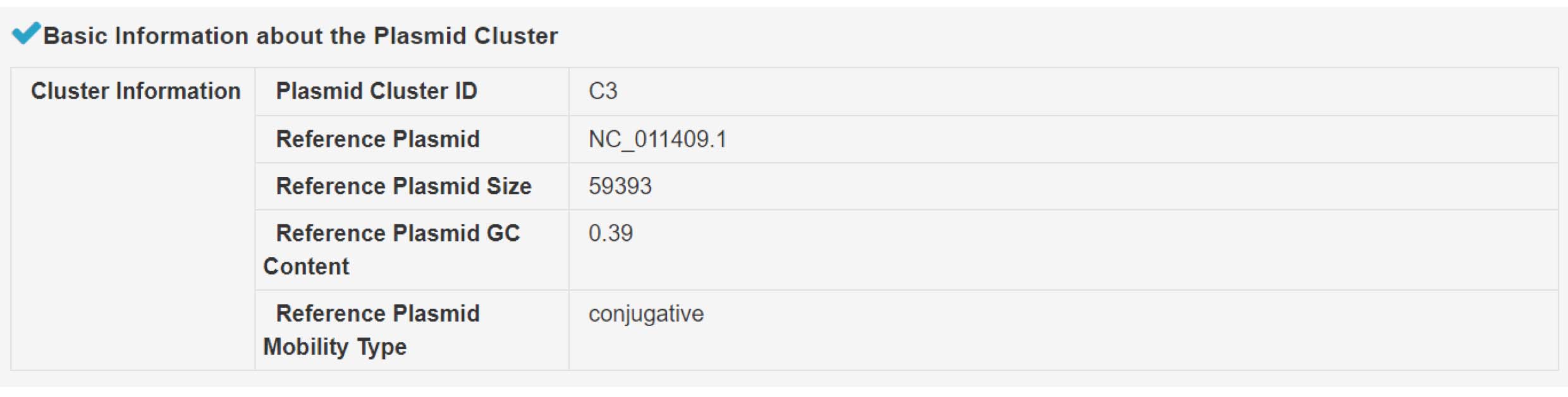
1) Summary of the plasmid cluster
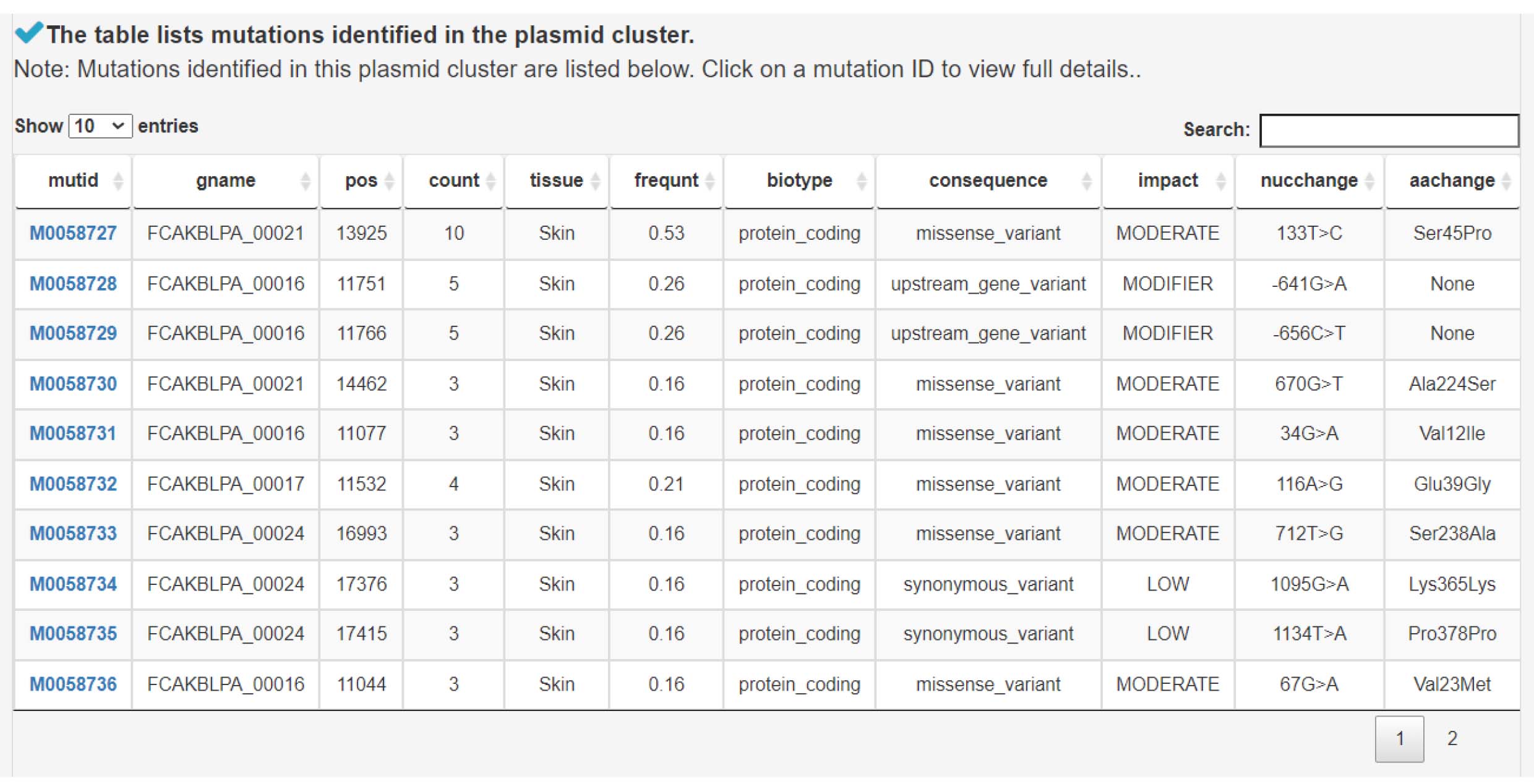
2) Mutation sites in the plasmid cluster
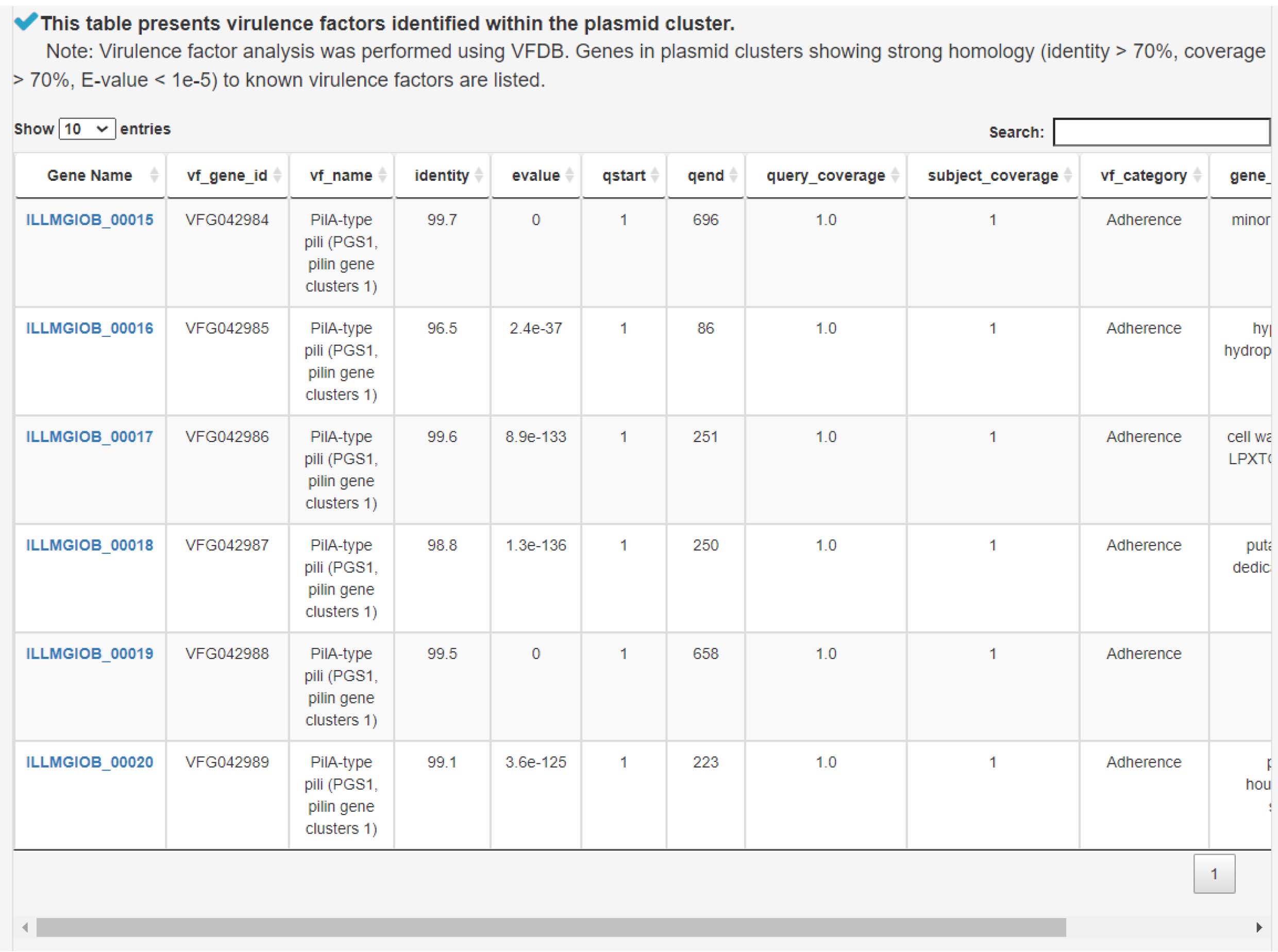
3) Analysis of virulence factors contributing to bacterial pathogenicity
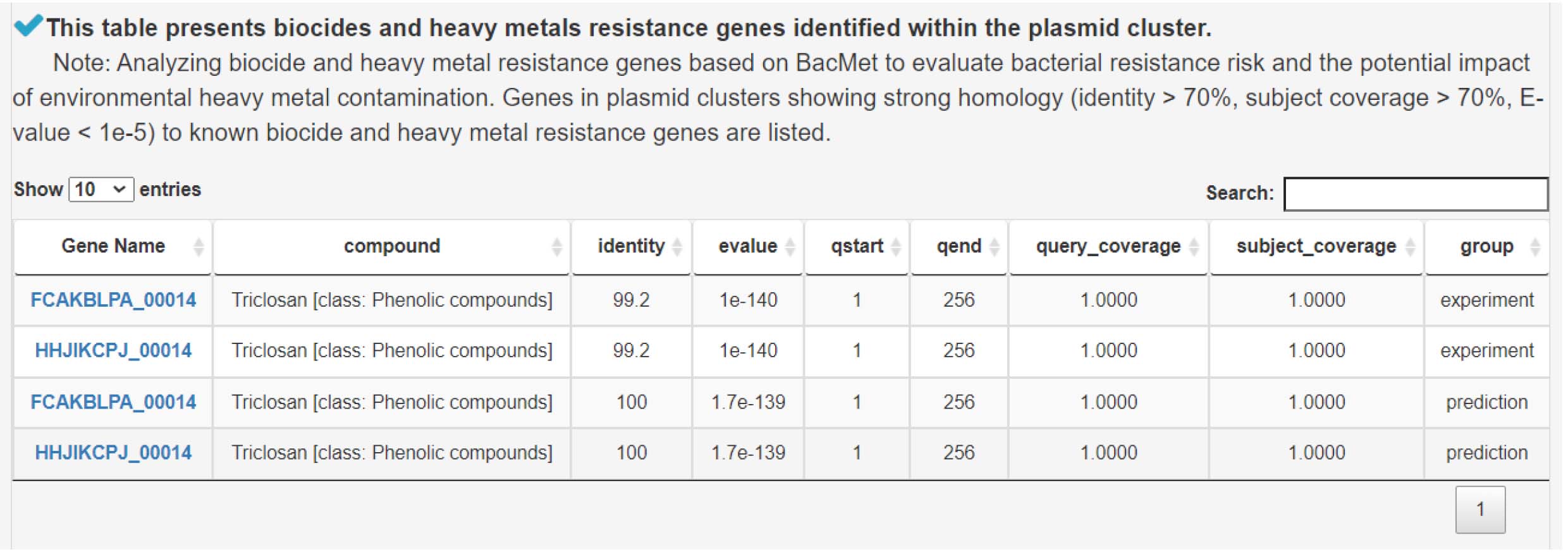
4) Analysis of biocide and heavy metal resistance genes to assess antimicrobial risk and environmental impact
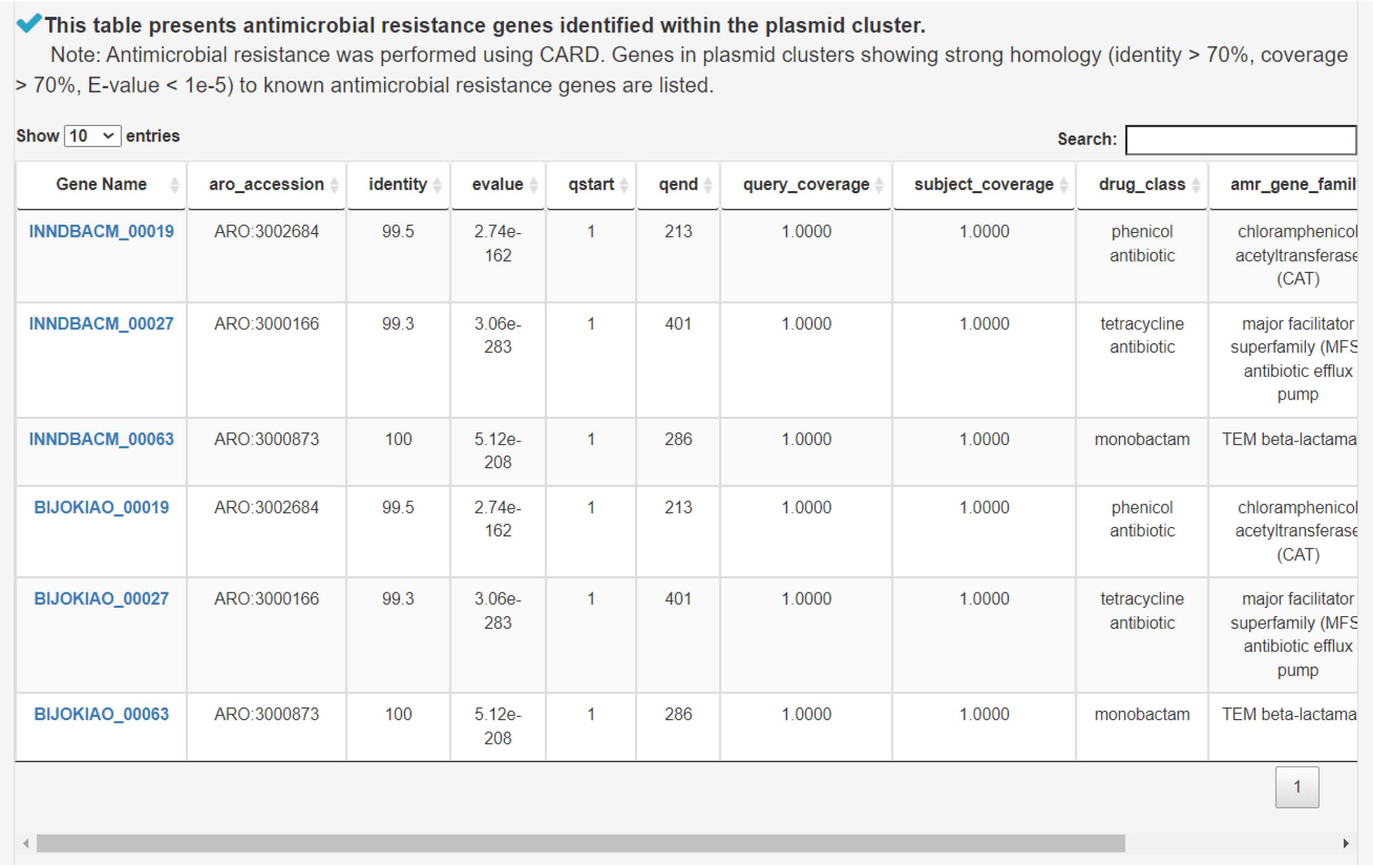
5) Analyzing antimicrobial resistance genes to assess bacterial resistance to antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents
6) Analysis of pathogenicity genes to explore pathogen-host interactions
7) Analyzing carbohydrate-active enzyme genes to uncover mechanisms of nutrient degradation
8) Analyzing transport proteins to understand bacterial strategies for substrate uptake and detoxification
Download data and contact us
All related files can be downloaded in the download page (download page)
The users can contact us for suggestions and comments (contact page)